Breast Cancer Detection Using Thermal Infrared Images
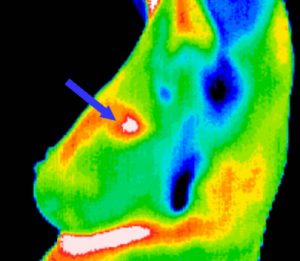
Today, one of the most common cancers identified in women is breast cancer. Several standard screening techniques are used for early detection of breast cancer such as Mammography and Thermography. Thermographies are thermal infrared images that are used to detect lesions in breasts. These Thermographies detect the temperature of the different regions of the breast. Regions with warmer temperature are more likely to contain tumors than normal tissue. A dynamic Thermography procedure is used to detect the difference between normal and abnormal tissues. This procedure uses thermal infrared cameras to generate infrared images at fixed time which contains a sequence of infrared images. The dynamic Thermography technique has several advantages:
- It is less expensive than the mammography and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- It is non-invasive, non-ionizing
- It is a safe diagnostic procedure, in which patients feel no pain
The discipline of the work of dynamic Thermography is based on two facts:
- the temperatures of breast cancer regions are warmer than the surrounding tissues, and (2) metabolic heat and blood per-fusion rates generation in tumors are much higher than the rates of normal regions.
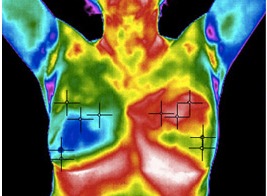
While using dynamic Thermography method, the variation of temperature between healthy and unhealthy breasts can be recorded by thermal infrared cameras. Using this method may increase the detection findings of static infrared images by exploiting cooling or heating procedures as a superficial stimulus to improve the thermal contrast and thermally exciting tissues of patients’ breasts. It is important to highlight that since the temperature range of body is 36.5∘C to 37.5∘C and higher temperature range may harm the living tissues in the breasts, hence the cooling procedure is much safer than the heating procedure. This cooling procedure proceeds as follows:
- After applying the cooling procedure on the breasts, the temperature of healthy tissues decreases with an attenuation of vascular diameter
- In turn, the temperature of abnormal tissues remains unaltered (or it increases with a vascular dilation)
- The findings of the analysis of the similarity (or the dissimilarity) between infrared images acquired before and after the cooling procedure can be exploited to reveal breast cancer.
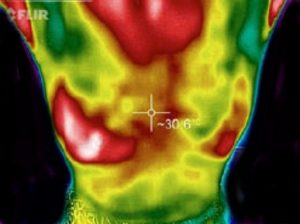
Since 1990s, respective techniques have been presented for the early detection of breast cancer, such as mammography and MRI. Both techniques have their own drawbacks. Mammography is the standard method for early detection of breast cancer, but its main drawback is that it may produce a large number of false positives. In spite of mammography, the MRI technique is added to mammography technique for women with genetic mutations. However, its main limitation is that it has a limited spatial resolution, yielding a low sensitivity for sub-centimeter lesions. Several other techniques have been suggested to overcome the limitations of aforementioned methods (Mammography and MRI). The infrared thermal imaging method can analyze breast cancer using dynamic Thermograms and also it can selectively optimize the contrast in areas of dense tissues in young women. By taking into account the lateral views and the frontal views of the breasts, scientists proposed a new method for extracting the region of interest (ROI) from breast Thermograms. The obtained ROIs help physicians to differentiate between the bio-markers of normal and abnormal cases. Saniei et al. [27] presented a five-step approach for analyzing the thermal images for cancer detection. The five steps are listed in the following paragraph:
- The breast region is extracted from the infrared images using the connected component labeling method
- The infrared images were aligned using a registration method
- The blood vessels were segmented using morphological operators
- For each vascular network, the branching points were exploited as thermal minutia points
- The branching points were fed into a matching algorithm to classify breast regions into normal or abnormal, achieving a sensitivity of 86% and a specificity of 61%